Sea Floor Spreading Rates 110 85 Mya

Figs 3 and 5 seismic refraction velocity depth data e g.
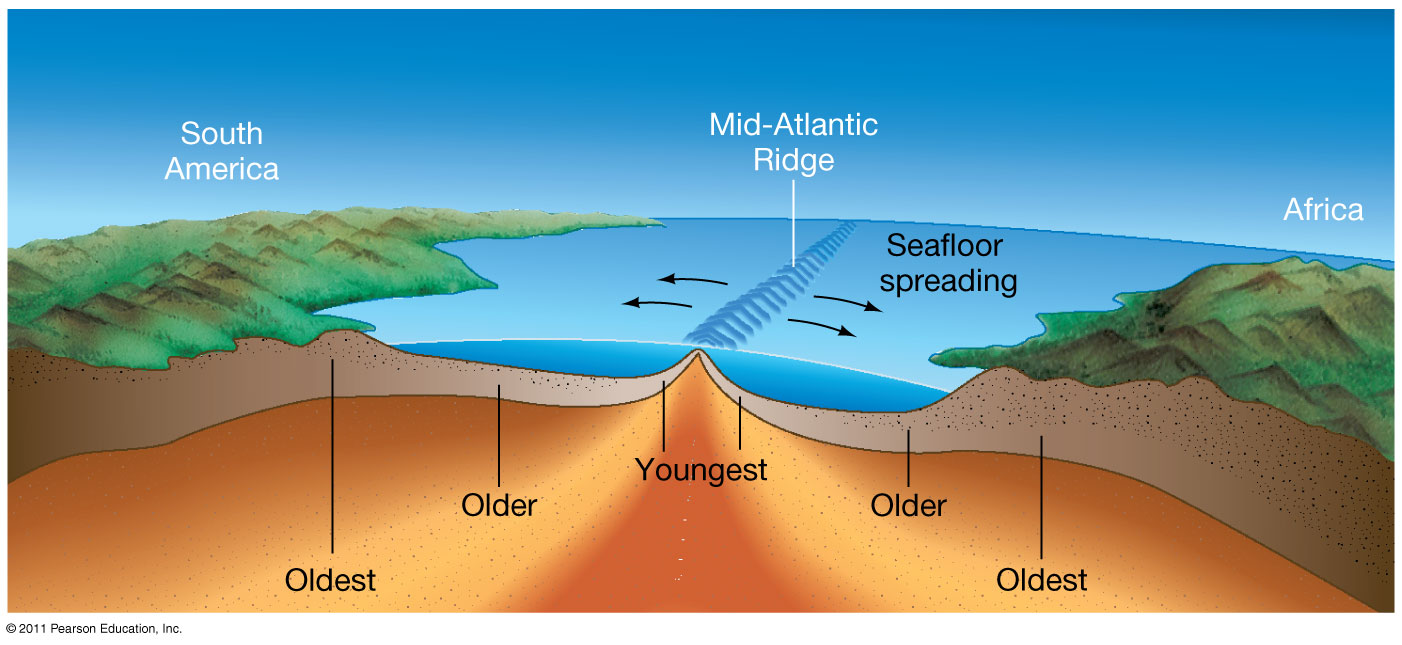
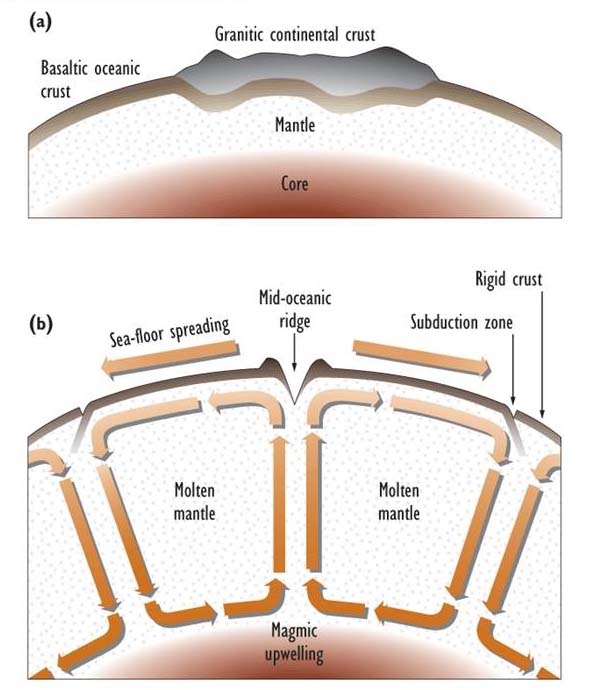
Sea floor spreading rates 110 85 mya. Measure from the center of the spreading center to a known age point on the plate rather than from 65 ma on the eastern plate to 65 ma on the western. This idea played a pivotal role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics which revolutionized geologic thought during the last quarter of the 20th century. Spreading rates determine if the ridge is fast intermediate or slow. 1cm yr to 10 cm yr.
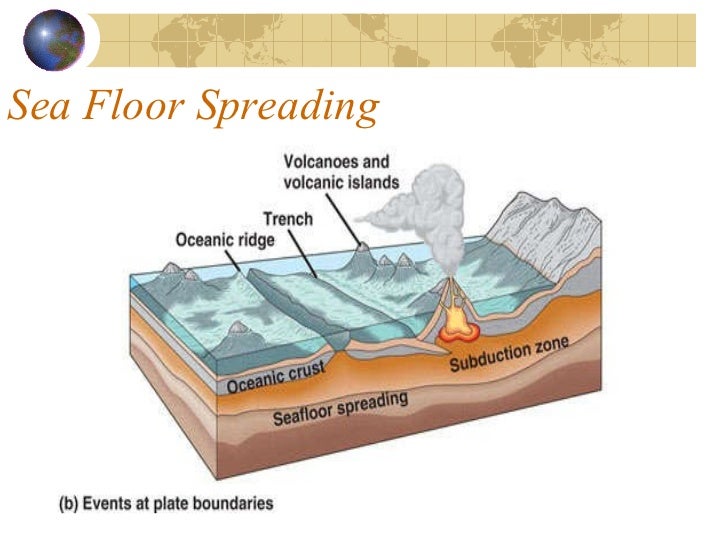
Make the necessary measurements to calculate the spreading rates on either side of the spreading center during the most recent 40 ma i e. Seafloor spreading occurs along mid ocean ridges large mountain ranges rising from the ocean floor. Seafloor spreading theory that oceanic crust forms along submarine mountain zones and spreads out laterally away from them. Spreading rate is the rate at which an ocean basin widens due to seafloor spreading.
Use the above equation to calculate spreading rate. High cretaceous ocean crust production rates have been causally linked to high global sea level and global co 2 due to increased outgassing. A constant rate of ridge production has im portant implications for models of sea level and p co2 among other phenomena that have been linked to variations in global rates of seafloor spreading. While we can identify a seafloor spreading sequence with a general ene trend along the antarctic margin figs 4 and 5 from west to east we can observe an increase in spreading rate and tectono magmatic variations across the spreading segments from the potential field data e g.
The rate at which new oceanic lithosphere is added to each tectonic plate on either side of a mid ocean ridge is the spreading half rate and is equal to half of the spreading rate. R d t or r 9 5 10 7 cm 6 5 10 7 years 1 46 cm yr. The rates differ between the 3 spreading centers and along their respective boundaries. Ranges of spreading throughout the world s oceans.
This data table provides spreading rates for divergent boundaries spreading centers in the pacific atlantic and indian oceans. Slower spreading rates lead to a rough topography because the tectonic plate is allowed to cool before moving away from the ridge.