Sea Floor Spreading Occurs At What Landform

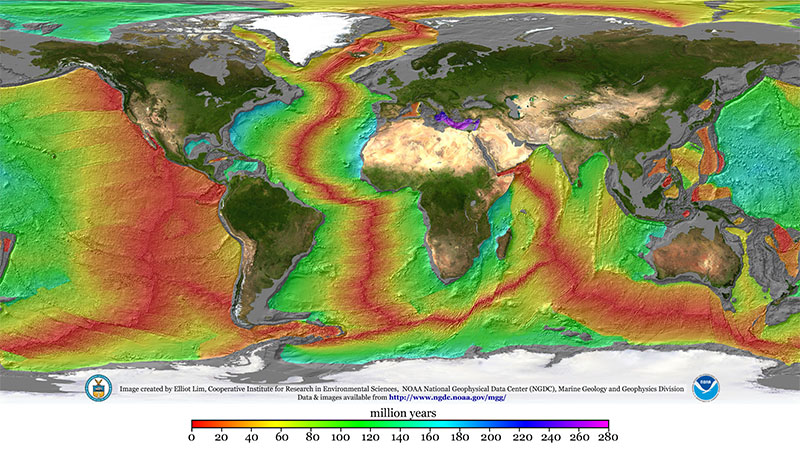
For instance the atlantic ocean is believed to be expanding because of its few trenches.
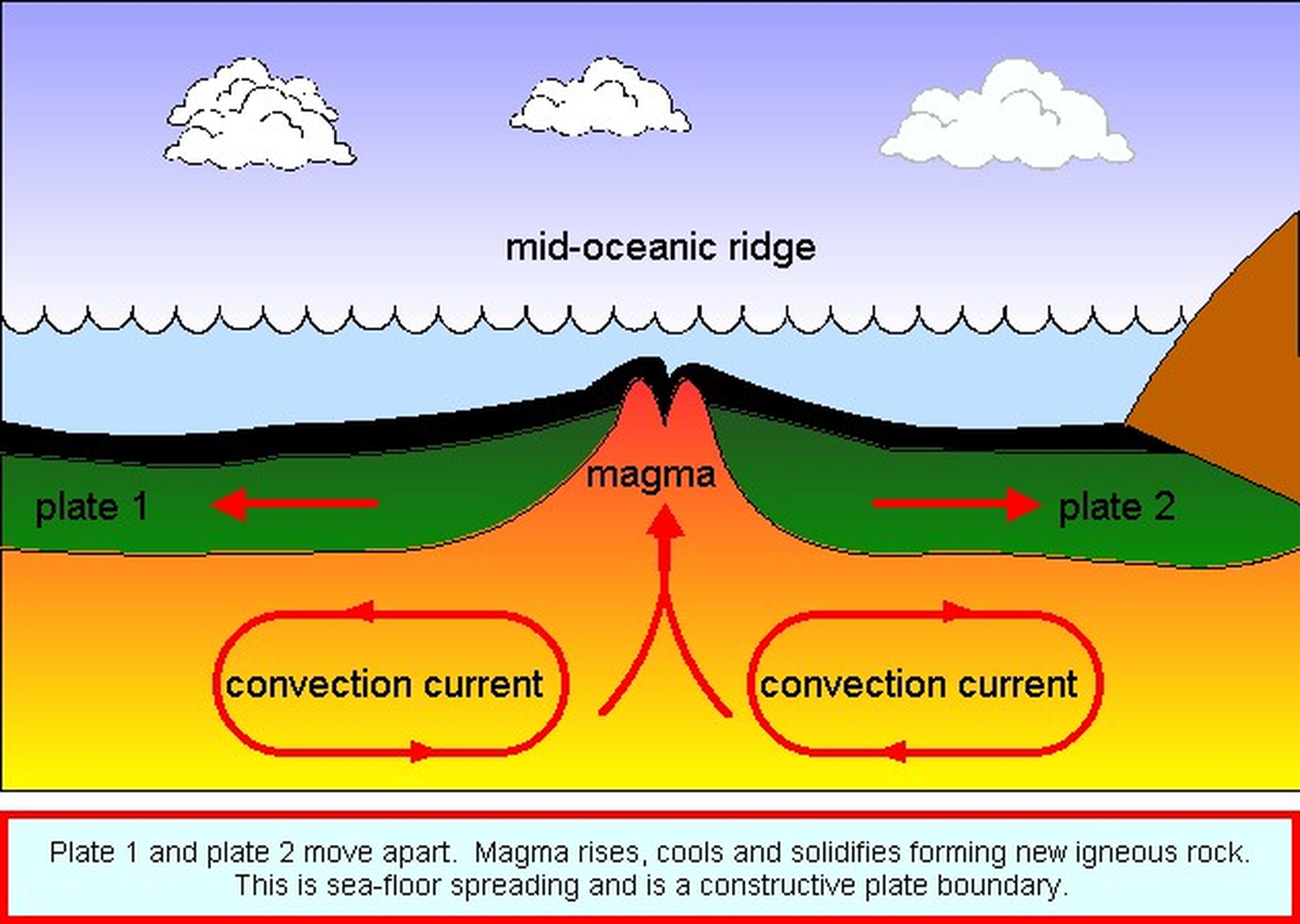
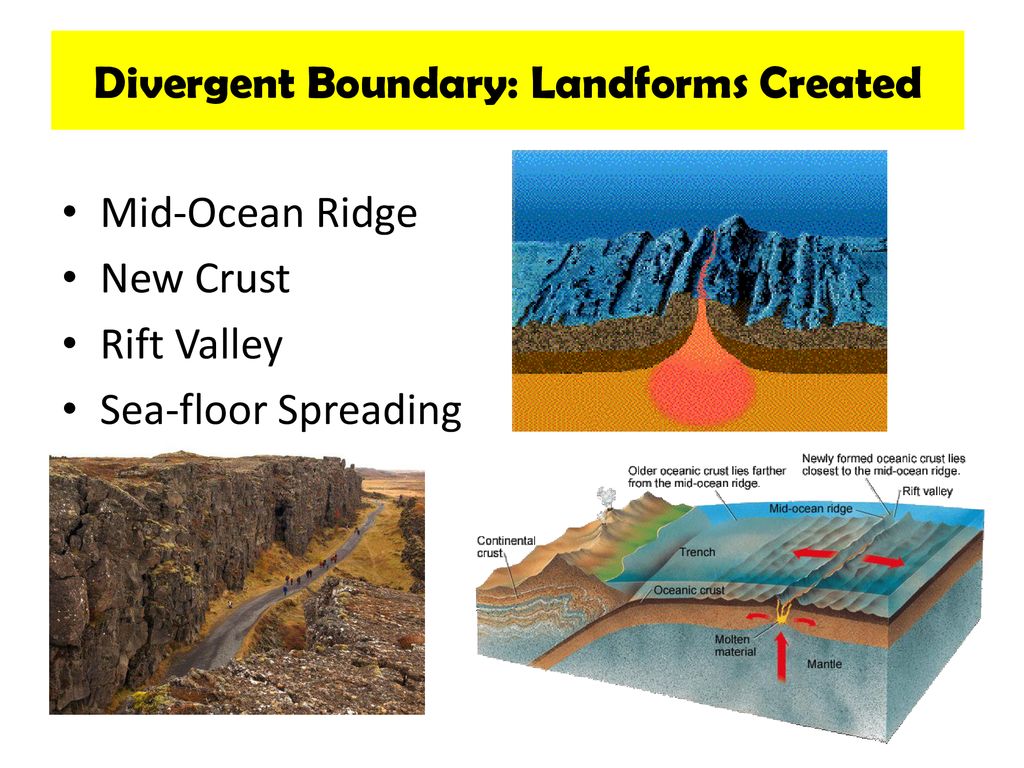
Sea floor spreading occurs at what landform. Sea floor spreading occurs when the sea floor spreads apart along divergent boundaries and forms the mid ocean ridge. Seafloor spreading is a process that occurs at mid ocean ridges where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge. As the magma is thrust up and hardens it forms new crust and the ocean floor on both sides of the mid ocean ridge move outward. Due to this continuous seafloor spreading occurs and makes atlantic ocean floor to be connected to other continental crust making the ocean gets wider over the time.
As the plates in this space continue to diverge they do so in opposite. What happens to a divergent boundary on the seafloor. Seafloor spreading occurs at a diversion boundary. As the plates split apart they do so at differing speeds creating space anywhere from a few to several hundred miles between spreading margins.
At this point tectonic plates pull away from each other and the gaps fills with magma from the mantle. Seafloor spreading occurs along mid ocean ridges large mountain ranges rising from the ocean floor. This graphic shows several ocean floor features on a scale from 0 35 000 feet below sea level. 2 plates slide past each other is opposite directions.
Most transform boundaries consist of short faults on the seafloor occurring near mid ocean ridges. Mid ocean ridge warmer less dense and younger trenches colder more dense younger. Earlier theories by alfred wegener and alexander du toit of continental drift postulated that. Subduction and sea floor spreading are processes that could alter the size and form of the ocean.
The land form is a fault and the natural events it maeks are tsunamis or earthquakes. Magma is pushed up through cracks in the crust along the mid ocean ridge. This idea played a pivotal role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics which revolutionized geologic thought during the last quarter of the 20th century. Continental shelf 300 feet continental slope 300 10 000 feet abyssal plain 10 000 feet abyssal hill 3 000 feet up from the abyssal plain seamount 6 000 feet.
The following features are shown at example depths to scale though each feature has a considerable range at which it may occur.