Sea Floor Spreading Is The Tectonic Process That Occurs A
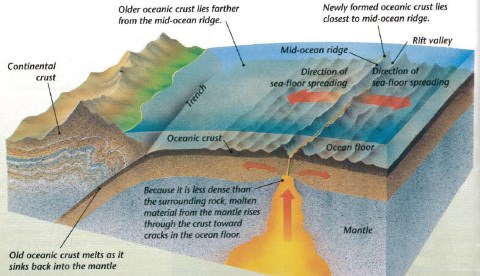
Seafloor spreading occurs along mid ocean ridges large mountain ranges rising from the ocean floor.
Sea floor spreading is the tectonic process that occurs a. Seafloor spreading theory that oceanic crust forms along submarine mountain zones and spreads out laterally away from them. Seafloor spreading is a process that occurs at mid ocean ridges where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge. For instance the atlantic ocean is believed to be expanding because of its few trenches. This idea played a pivotal role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics which revolutionized geologic thought during the last quarter of the 20th century.
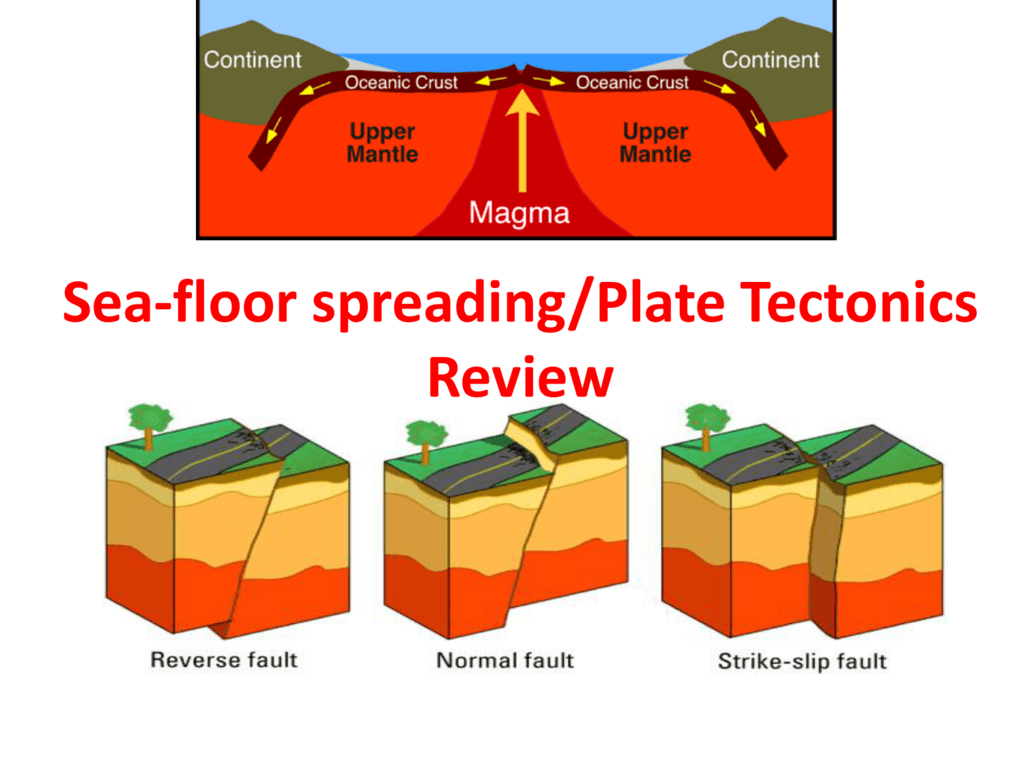
The motivating force for seafloor spreading ridges is tectonic plate slab pull at subduction zones rather than magma pressure although there is typically. When oceanic plates diverge tensional stress causes fractures to occur in the lithosphere. When oceanic plates diverge tensional stress causes fractures to occur in the lithosphere. Due to this continuous seafloor spreading occurs and makes atlantic ocean floor to be connected to other continental crust making the ocean gets wider over the time.
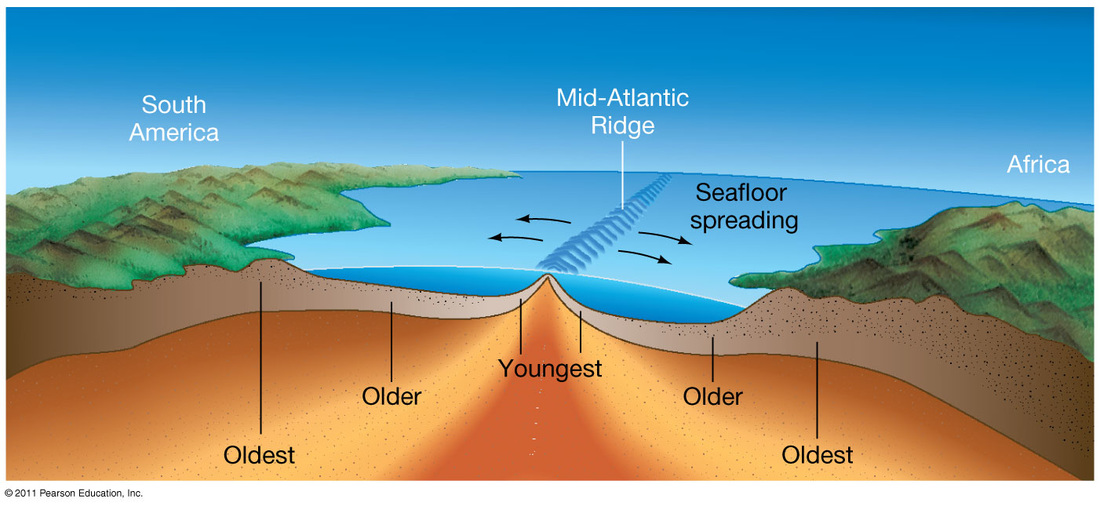
These age data also allow the rate of seafloor spreading to be determined and they show that rates. As upwelling of magma continues the plates continue to diverge a process known as seafloor spreading samples collected from the ocean floor show that the age of oceanic crust increases with distance from the spreading centre important evidence in favour of this process. Seafloor spreading helps explain continental drift in the theory of plate tectonics. Seafloor spreading is credited for the formation of the red sea as a result of the movement of the arabian and african tectonic plates away from each other.
Subduction and sea floor spreading are processes that could alter the size and form of the ocean.









.PNG)






