Sea Floor Spreading Effect On Sea Level

Alfred wegener a german meteorologist born in 1880 developed the idea of continental drift.
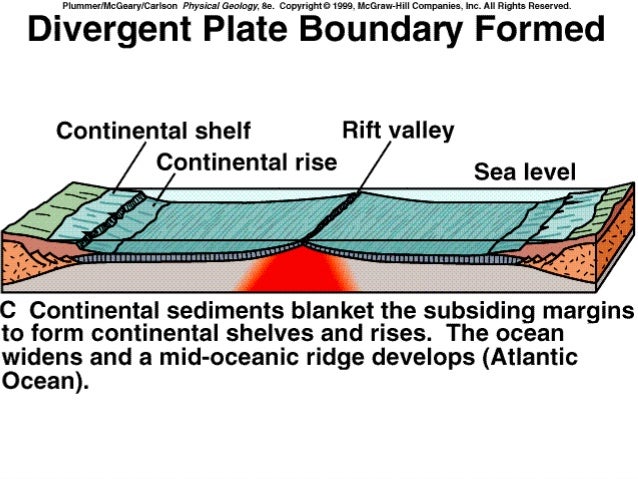
Sea floor spreading effect on sea level. The following features are shown at example depths to scale though each feature has a considerable range at which it may occur. We present a theory for divergent seafloor spreading which predicts that transient surges in spreading rate would cause geodynamic sea level rise rates approximately equal to the transient surge velocity at the ridge crest multiplied by the aspect ratio of the spreading plate i e a surge velocity of 3 cm yr acting on a plate thickness 100 km and width 3000 km would produce a geodynamic. While eustatic sea level is measured from a reference point at the center of the earth relative sea level is the position of mean sea level relative to the position of the crust fig. 21 since the new oceanic basins are shallower than the old oceanic basins the total capacity of the world s ocean basins decreases during times of active sea floor spreading.
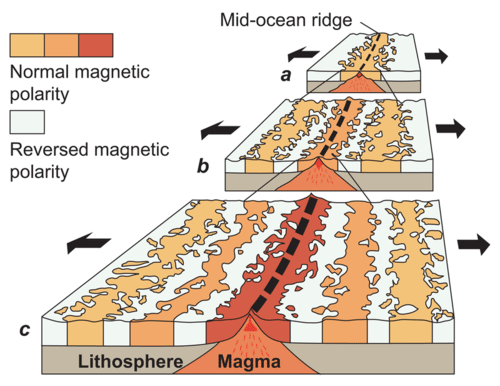
Figure showing sea floor spreading the intense heat generated by radioactive substances in the mantle beneath the lithosphere seeks a path to escape and forms convection currents. The differences in spreading rates affect not only the geometries of the ridges but also the geochemistry of the basalts that are produced. He suggested that continents moved around the earth like giant rafts. Basalt the once molten rock that makes up most new oceanic crust is a fairly magnetic substance and scientists began using magnetometers to measure the magnetism of the ocean floor in the 1950s what they discovered was that the magnetism of the ocean floor around.
A dramatic proof of sea floor spreading was discovered in the mid 1960s when data revealed alternating stripes of magnetic orientation on the sea floor parallel to the mid ocean ridges and symmetric across them that is a thick or thin stripe on one side of the ridge is always matched by a similar stripe at a similar distance on the other. Fellow scientists at the time thought the theory was ludicrous. Continental shelf 300 feet continental slope 300 10 000 feet abyssal plain 10 000 feet abyssal hill 3 000 feet up from the abyssal plain seamount 6 000 feet. Therefore vertical movements of the crust through tectonic subsidence or uplift can produce localized effects of relative sea level rise or fall e g.
Vine f in abstracts of nato symposium continental drift sea floor spreading and plate tectonics implications for the earth sciences newcastle 1972. This graphic shows several ocean floor features on a scale from 0 35 000 feet below sea level.